[ad_1]
Figuring out the Age of Farm Animals by their Tooth
U. S. Division of Agriculture Farmers’ Bulletin No. 1721, March 1934 by George W. Pope, chief, Subject Inspection Division, Bureau of Animal Trade
Significance of Figuring out the Age of Farm Animals
The productive lifetime of cattle is relatively transient, the peak of their usefulness being restricted to a couple years. For that reason the returns from livestock are inclined to lower with superior years. The age of animals, due to this fact, is a matter of utmost significance to the breeder, the vendor, and the client.
Bodily adjustments inside the physique are fixed. They have an effect on the overall outward look and disposition and, inside sure limitations, it isn’t tough by mere common look to differentiate the younger animal from one which has reached maturity, and even to find out the approximate age of an previous animal. Modifications which happen within the enamel, nonetheless, afford the most effective alternative of figuring out the age.
Establishing the age of cattle by the looks of the enamel isn’t any new factor. The potential of judging on this method apparently was well-known in historic days. The previous saying, “Don’t look a present horse within the mouth,” is attributed to Saint Jerome, of the fifth century, who used this expression in certainly one of his commentaries. Definitely for generations the looks, improvement, and subsequent put on of the enamel has been acknowledged as a reliable technique of judging roughly the age of animals.
With a data of the age at which the enamel seem, the time for shedding non permanent or milk enamel and their alternative with everlasting enamel, and the adjustments in type which consequence from pure put on, the approximate age of cattle might be decided. Theoretical data, nonetheless, shouldn’t be enough, and anybody who would change into proficient should even have sensible expertise. This bulletin describes briefly the conventional processes of dentition and the adjustments which period brings about, and explains learn how to decide the ages of animals by inspecting their mouths.

Horses and Mules
The extraordinary observer can readily be taught to inform the age of horses or mules with appreciable accuracy till the animals have handed their eighth yr. Past this time even those that are skilled could discover it tough to find out the precise age.
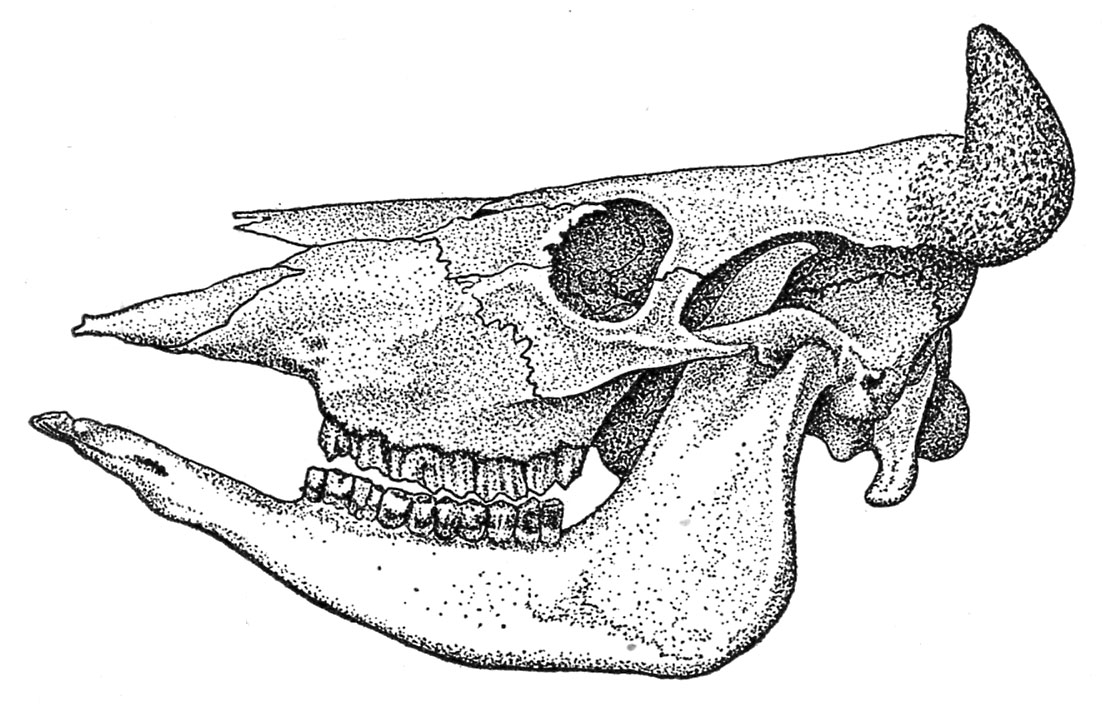
The mature male horse has 40 enamel (fig. 1). Twenty-four of those are molars or grinders, 12 are incisors or entrance enamel, and 4 are tushes or pointed enamel. The two central incisors are often called centrals or nippers; the subsequent 2, 1 on either side of the nippers, are known as intermediates or middles, and the final, or outer pair, the corners. The tushes are positioned between the incisors and the molars. They aren’t normally current within the mare, and accordingly she could also be thought-about to have a complete of 36 enamel reasonably than 40, as within the male.
The younger animal, whether or not male or feminine, has 24 non permanent enamel, generally known as milk enamel, as they’re much whiter than the everlasting enamel. These milk enamel encompass 12 incisors and 12 molars. The latter are the three again enamel on either side of each the higher and the decrease jaw. The milk enamel are shed and changed by everlasting enamel at pretty particular intervals, which function an index in figuring out the age of younger colts.

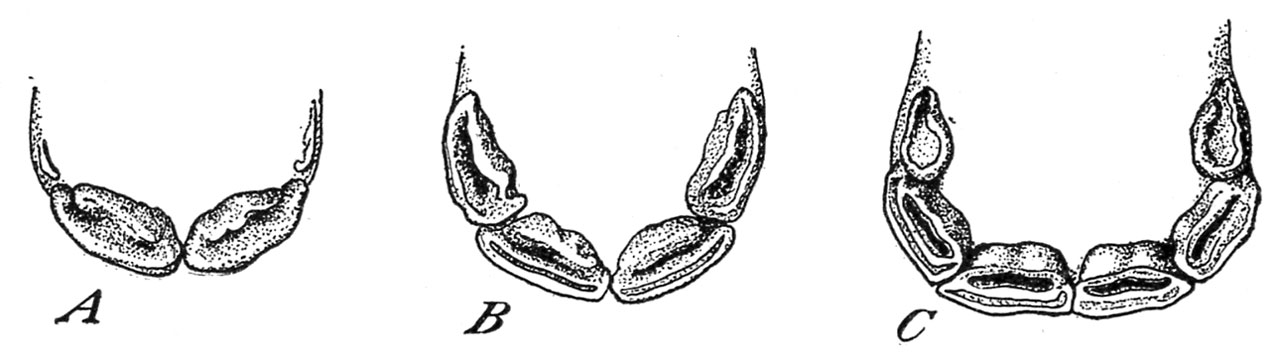
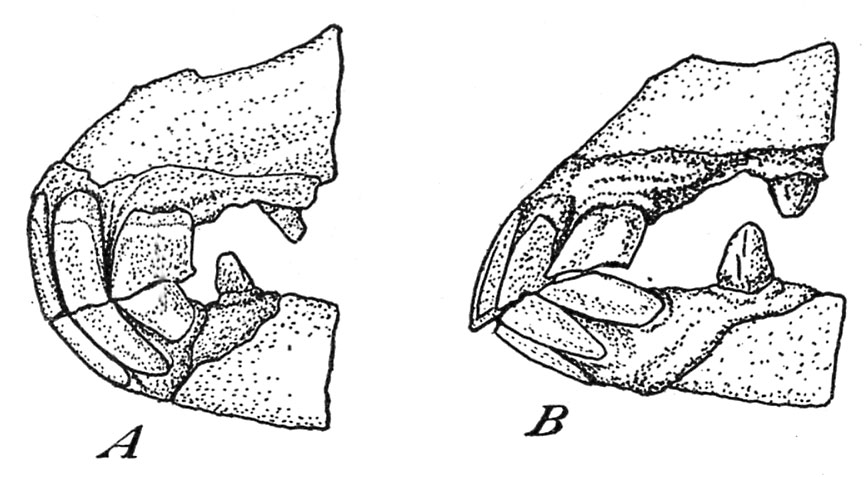
The non permanent central incisors or nippers could also be current at beginning (fig. 2, A); in any other case they seem earlier than the colt is 10 days previous. There are two in every jaw.
On the age of from 4 to six weeks the 2 non permanent intermediates, higher and decrease, seem (fig. 2, B). These enamel instantly adjoin the nippers.
When the colt is from 6 to 10 months previous the nook or outer incisors, two above and two beneath, are reduce (fig. 2, C). This provides the younger animal a full set of non permanent entrance enamel.
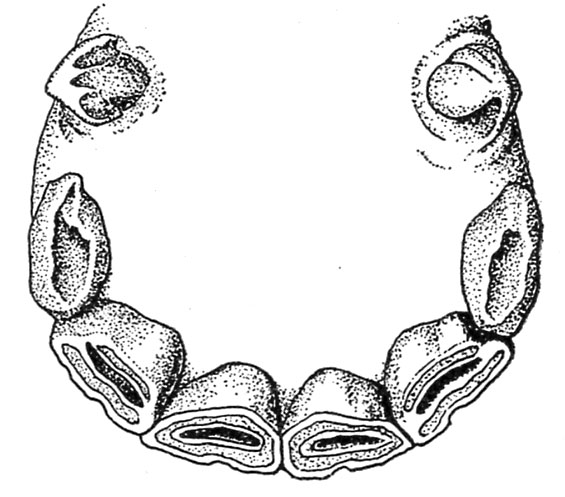
By the point the colt has reached the age of 1 yr the crowns of the central incisors present put on (fig. 3, A). In one other 6 months the intermediates or middles change into worn (fig. 3, B), and at 2 years all of the enamel are worn (fig. 3, C). Throughout the next 6 months there are not any adjustments which can distinguish the precise age. At about 2 1/2 years, nonetheless, the shedding of the milk enamel begins and at 3 years the non permanent central nipper, two above and two beneath, are changed by the everlasting central incisors.

At 4 years the 4 everlasting intermediates have taken the place of the 4 non permanent middles (fig. 4).
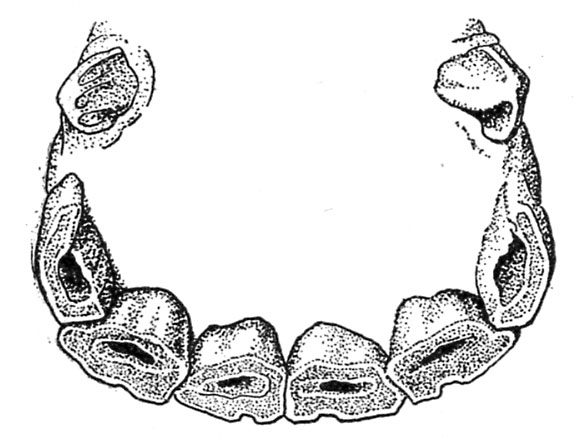
When the animal is about 4 1/2 years previous the shedding of the 4 corners begins, and at 5 years the everlasting enamel which change them are properly up however not involved (fig. 5).
In a 6-year-old horse the nook incisors are on a degree with the adjoining enamel, with a well-marked dental cavity or “cup” displaying virtually no put on (fig. 6). The nippers present put on over the complete floor; the “cup” although seen exhibits indications of gradual disappearance and at this stage is with out a hole.
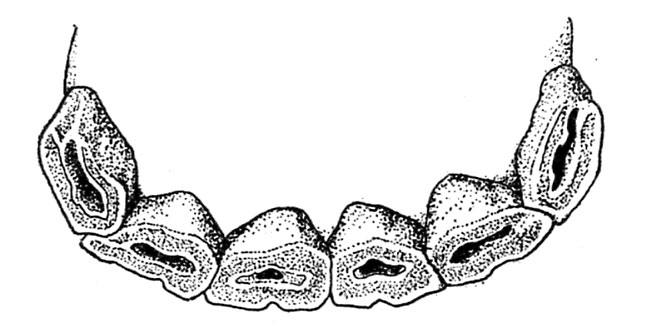

When the animal is 7 years previous, not solely the nippers but additionally the middles present put on (fig. 7). Every higher nook tooth has an indentation brought on by put on from the corresponding decrease tooth, leading to a downward triangular projection of the posterior edge. This projection is usually termed “dovetail” (fig. 8).
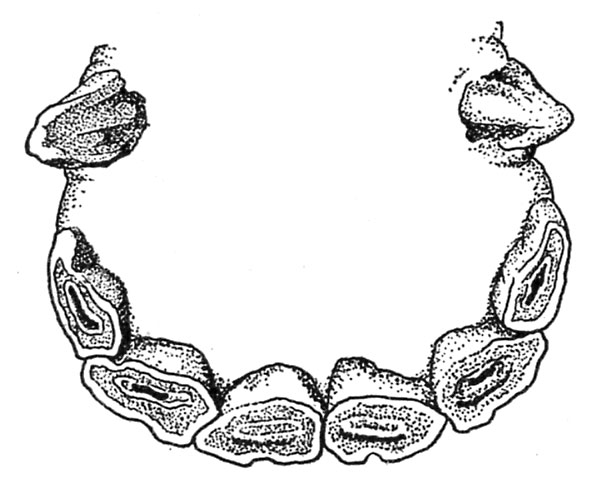
Within the 8-year-old horse all of the incisors are worn, the cup has fully disappeared from the nippers, however exhibits to a slight extent within the middles, and continues to be properly marked within the corners. At this stage what’s termed the “dental star” makes its look as a yellow transverse line simply again of the entrance fringe of the desk, or flat floor, of the nippers and middles (fig. 9).
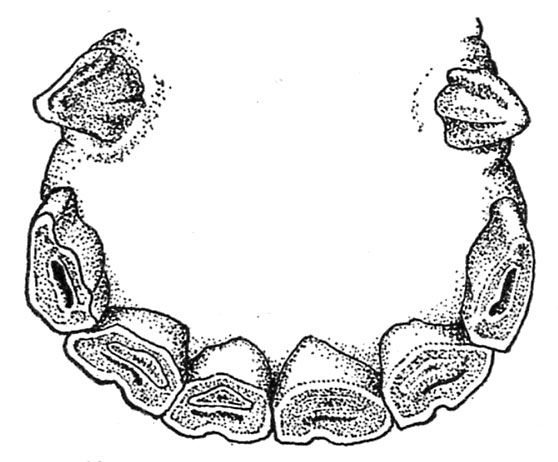
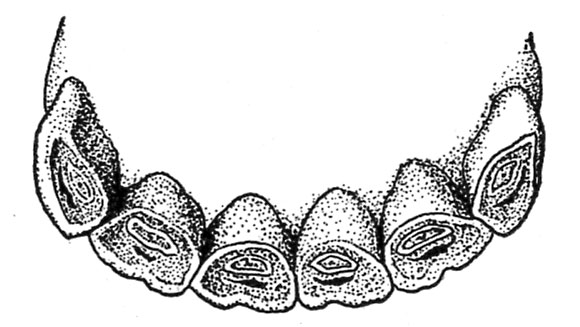

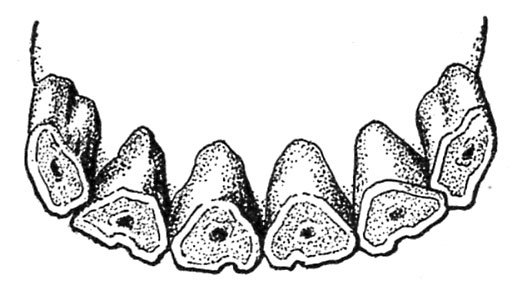
Between the ages of 9 and 13 years there’s a gradual change within the contour of the tables of the incisors. In a 9-year-old animal the nippers tackle a kind of rounded contour; the dental cavity or cup has disappeared from all however the corners; the dental star is present in each the nippers and middles and within the former is close to the middle of the desk (fig.10). At 10 years the middles change into rounded, and the dental star, now seen on all of the incisors, is close to the middle of each the nippers and middles (fig. 11). At 11 or 12 years the corners have a considerably rounded type, and the dental star approaches the middle of the desk (fig. 12). Because the horse reaches 13 years of age all of the decrease incisors are unmistakably rounded, the dental star is discovered within the heart of all of the tables, and the enamel rings which previously surrounded the cups have fully disappeared (fig. 13).


In a horse about 14 years of age the tables of the incisors start to alter from a rounded to a triangular contour. This alteration happens within the nippers at 14 years (fig. 14), within the middles at 15 years, and within the corners at 16 or 17 years (fig. 15).
Throughout the next 4 years after the looks of the triangle, there’s a gradual strategy of the tables to the type of a rectangle, as proven in determine 16. The enamel throughout this era are normally elongated and directed obliquely. The dental arch additionally turns into contracted and pointed and the beneath edges of the decrease jaw are skinny and sharp as in contrast with their look in a younger horse (fig. 17). Ought to the animal reside greater than 20 years, these circumstances change into extra marked and are accompanied by extreme put on and loosening or lack of molars.
Cattle
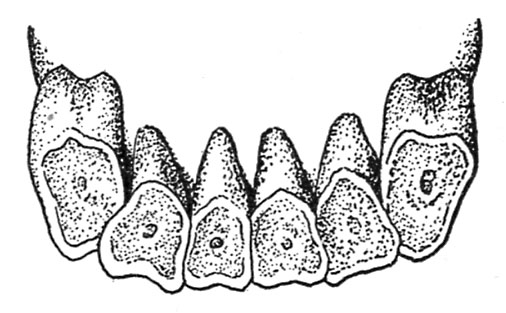
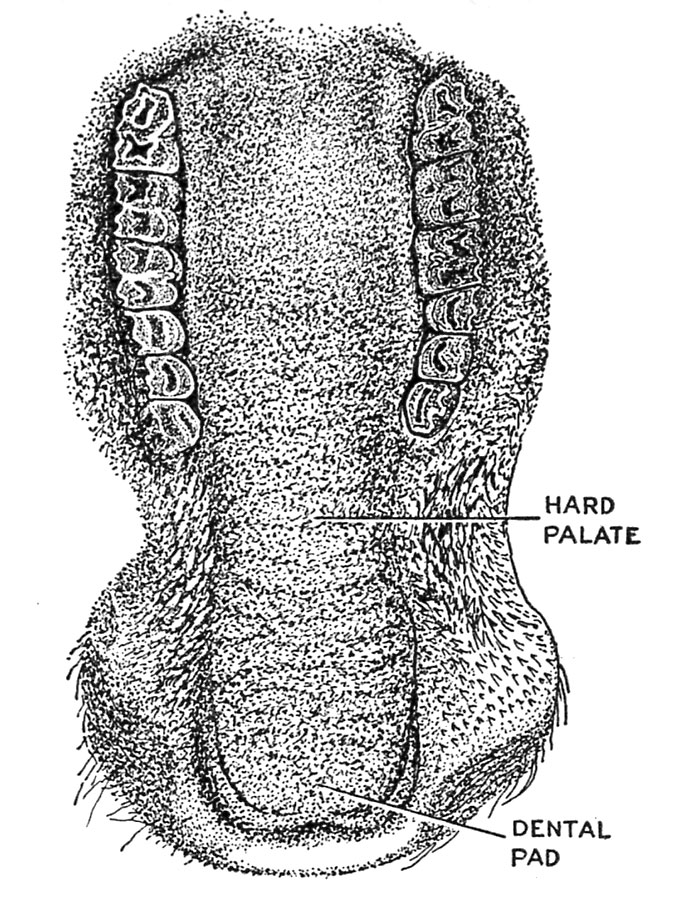
Cattle at maturity have 32 enamel, of which 8 are incisors. All incisors are within the decrease jaw (fig. 18). The 2 central incisors are known as pinchers; the subsequent two, first intermediates; the third pair, second intermediates or laterals; and the outer pair is called the corners. Rather than the higher incisor enamel there’s a thick layer of the arduous palate known as the dental pad (fig. 19).

Within the calf at beginning two or extra of the non permanent or first set of incisor enamel are current. Throughout the first month the complete eight incisors have appeared (fig. 20).
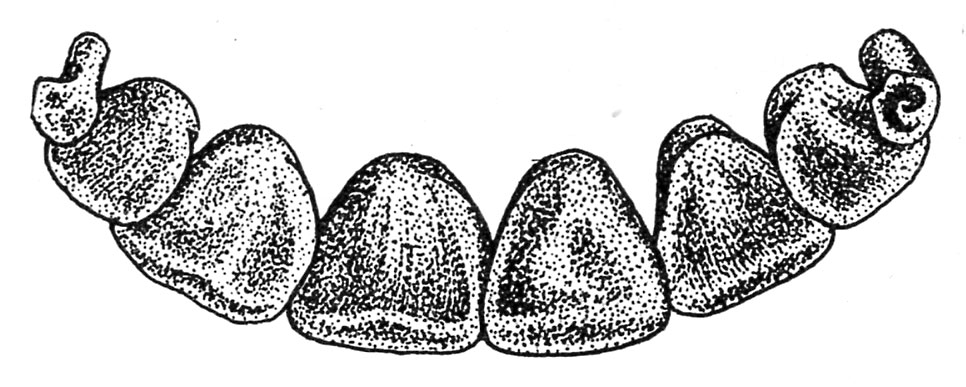
Because the animal approaches 2 years of age the central pair of non permanent incisor enamel or pinchers is changed by the everlasting pinchers. At 2 years these enamel attain full improvement (fig. 21).

At about 2 1/2 years the everlasting first intermediates, one on either side of the pinchers, are reduce and are normally totally developed at 3 years (fig. 22).
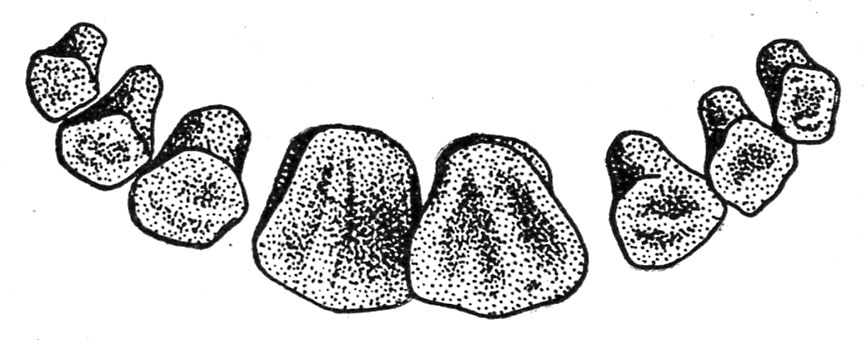
At 3 1/2 years the second intermediates or laterals are reduce. They’re on a degree with the primary intermediates and start to put on at 4 years (fig. 23).

At about 4 1/2 years the nook enamel are changed. At 5 years the animal normally has the complete complement of incisors with the corners totally developed (fig. 24).
At 5 or 6 years there’s a leveling of the everlasting pinchers, the pinchers normally being leveled at 6 years and each pairs of intermediates partially leveled and the nook incisors displaying put on.
At 7 or 8 years there’s a noticeable carrying of the pinchers; at 8 or 9 years, of the center pairs; and at 10 years, of the nook enamel.

After the animal has handed its sixth yr, the arch regularly loses its rounded contour and turns into almost straight by the twelfth yr (fig. 25). Within the meantime the enamel have regularly change into triangular in form, distinctly separated, and present progressive carrying to stubs. This situation turns into extra marked with growing age.

Sheep and Goats
Mature sheep and goats have 32 enamel, of which 24 are molars and eight are incisors (fig. 26). There are not any tusks and, like these of cattle, all of the incisors are within the decrease jaw. As within the case of cattle, additionally, the 2 central incisor enamel are known as pinchers; the adjoining ones, first intermediates, the third pair, second intermediates; and the outer ones, corners. The non permanent incisors are readily distinguished from the everlasting ones by their smaller measurement and milky whiteness.
Within the new-born animal not one of the enamel could have made their look although typically the 2 pinchers and in addition the 2 first intermediates are urgent by the gums and even have reduce by. In a number of days these enamel and the second intermediate incisors will seem, adopted considerably later by the corners, thus giving the animal, by the point it’s 3 months previous, a full set of fully developed non permanent incisor enamel, as proven in determine 27, A.
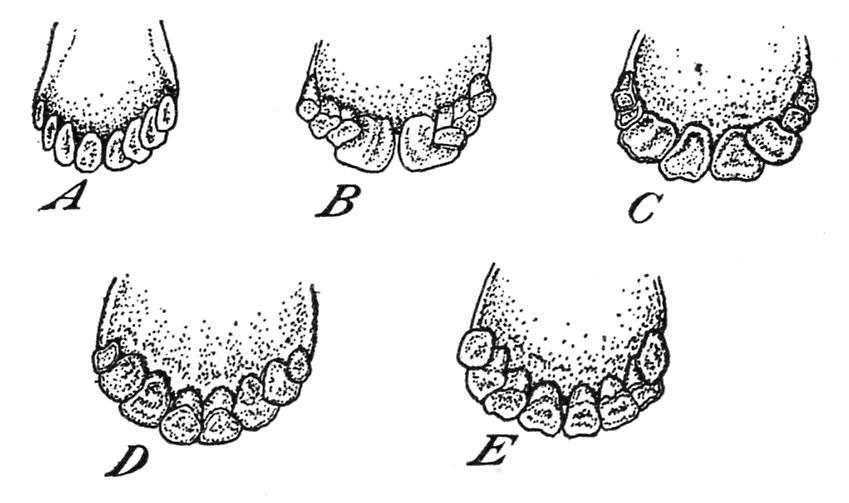
When the animal is between 12 and 15 months of age the non permanent pinchers are changed by the 2 everlasting ones (fig. 27, B).
The shedding of the primary non permanent intermediates and their alternative by everlasting enamel point out that the animal is approaching its second yr (fig. 27, C).
The alternative of the second non permanent intermediates by the everlasting ones takes place when the animal is about 3 years previous (fig. 27, D).
The 2 non permanent nook incisors are changed by everlasting enamel because the sheep reaches the age of 4 years. All of the everlasting enamel are then current, and the animal has what’s termed a “full mouth” (fig. 27, E.)
After this time there’s a distinct and progressive enhance in measurement of the areas between the enamel, which regularly change into worn to stubs and continuously attain an unnatural and uneven size. In previous sheep some enamel could also be damaged or free; in such circumstances the animal is alleged to have a damaged mouth.
Swine
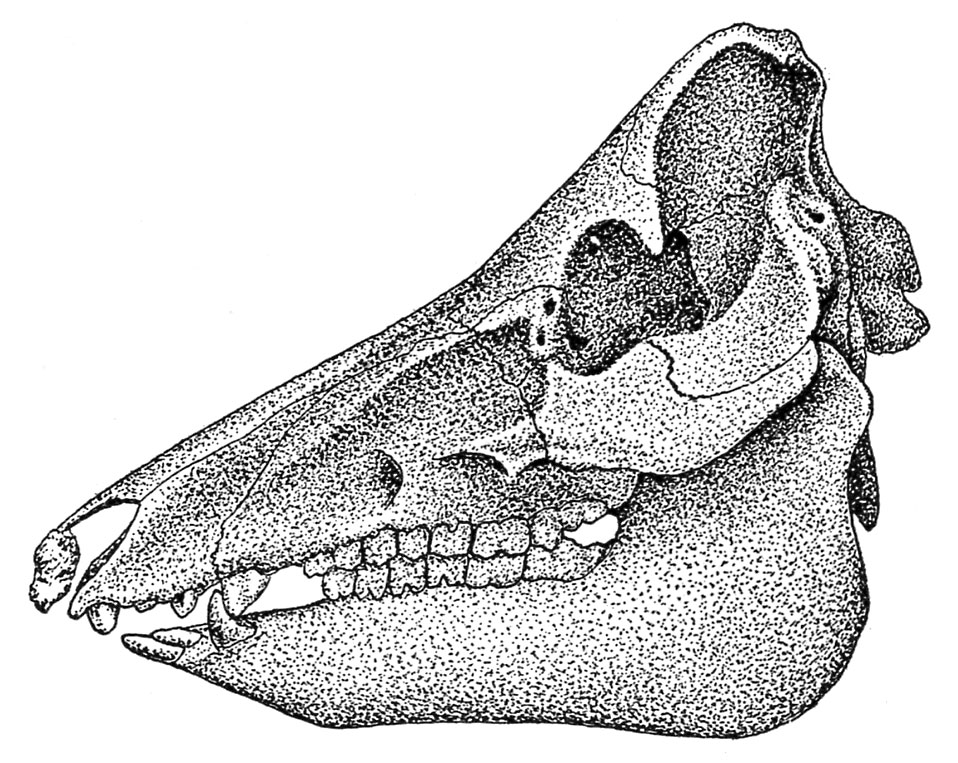
A mature hog has 44 enamel (fig. 28). Of those, 12 are entrance enamel or incisors, and 6 are within the higher and 6 within the decrease jaw. 4 others lie within the open areas again of the incisors and are often called tusks, or tushes. They’re normally extra distinguished within the male than within the feminine. Again of every tush is a tooth generally known as the premolar, and instantly again of this on either side of the higher and decrease jaws there are 6 molars, the primary 3 in every row typically being termed premolars. As within the horse, the incisors are grouped in three pairs in every jaw and are termed centrals, intermediates, and corners in accordance with their relative positions.
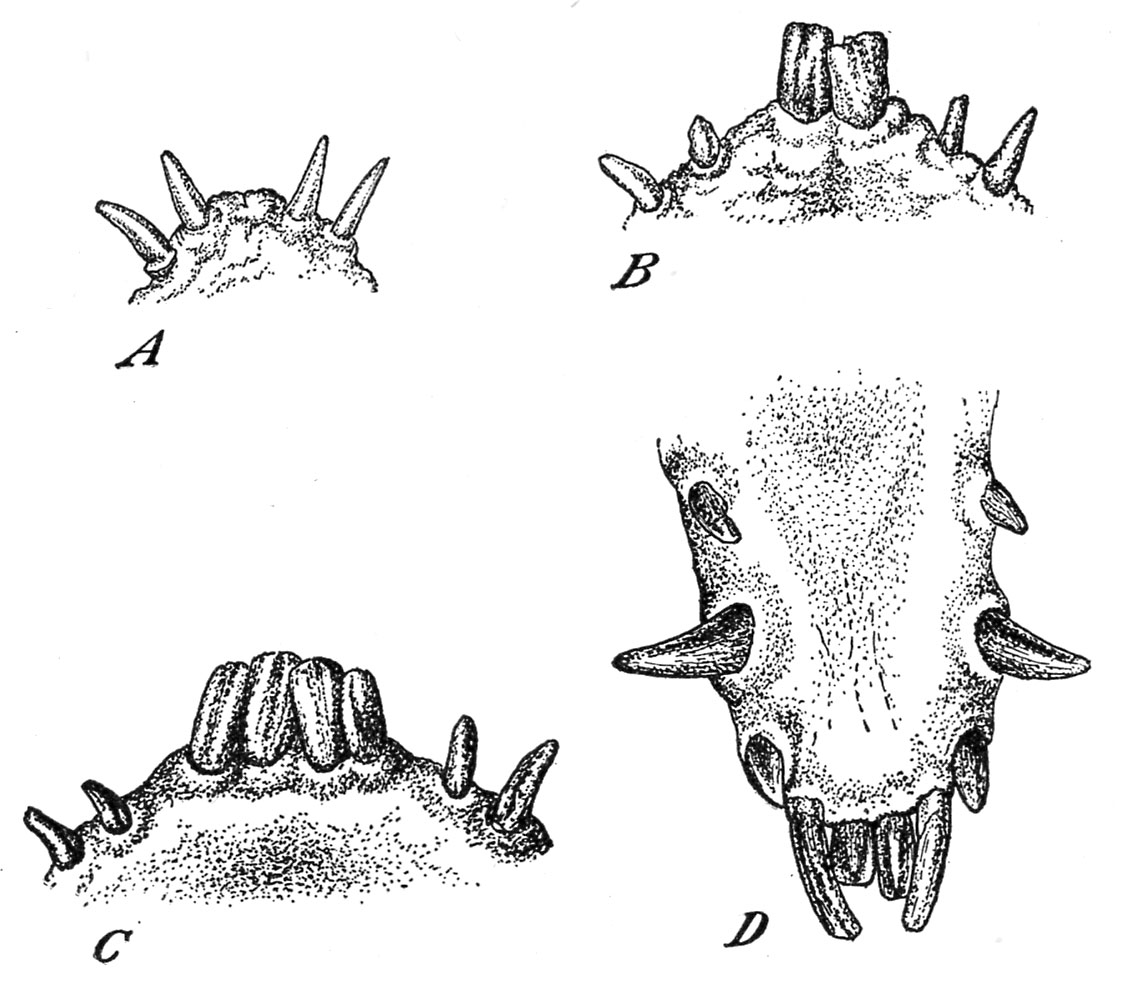
The younger pig at beginning normally has 8 enamel. These encompass the two tusks and a couple of nook incisors on every jaw. They’re all sharply pointed and are typically often called needle enamel (fig. 29, A). It’s a frequent observe to chop them off, about midway between the gum and level of the tooth, within the new-born pig, with the intention to keep away from discomfort and damage to the nursing sow.
When the pig reaches the age of 4 or 5 weeks the central non permanent incisors seem, two within the higher and two within the decrease jaw (fig. 29, B).
Because the animal approaches the age of 6 to eight weeks the 2 intermediate incisors may have reduce by the gums of the decrease jaw between the corners and the centrals and will probably be totally grown at 3 months (fig. 29. C).
Because the pig passes 6 months of age the non permanent nook incisors are shed, and the everlasting corners seem. Shortly after 9 months the everlasting tusks take the place of the non permanent tusks. At roughly 12 months the central everlasting incisors change the non permanent centrals, and the decrease enamel seem as proven in determine 29, D.
Through the subsequent 3 months the primary 3 non permanent molars, on either side of higher and decrease jaw, will probably be shed. These are instantly again of the premolars, which in flip are again of the tusks. When these non permanent molars, 12 in all, have been changed by everlasting molars, the pig has attained the age of at the very least 15 months.
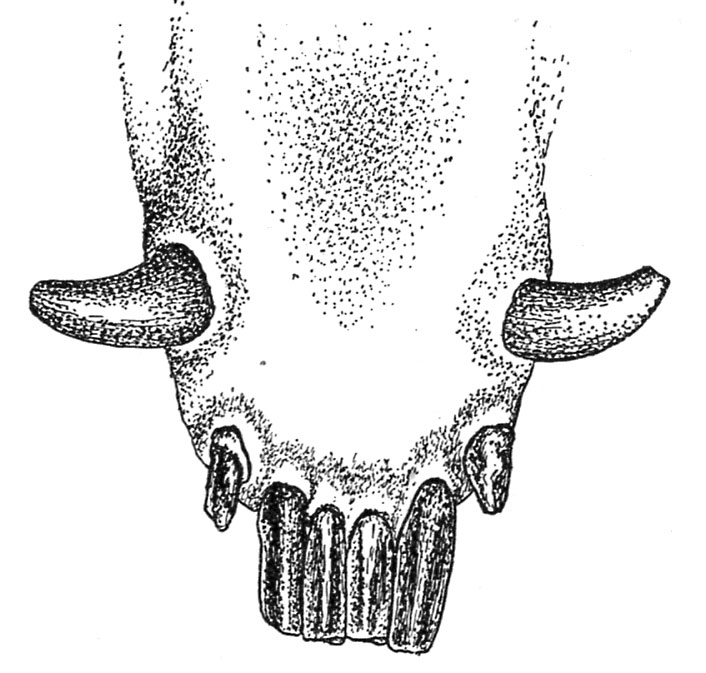
As a rule the shedding of the non permanent intermediate incisors and the looks of their locations of the everlasting ones are indications that the hog is roughly 18 months of age. By the point the animal has reached the age of 20 months these intermediate incisors will probably be consistent with the centrals (fig. 30).
As there isn’t any additional shedding or eruption of enamel, the age of hogs past 20 months of age can’t be so simply estimated. At 2 years, nonetheless, the incisors, together with the intermediates, will present put on, and the sixth or final molars (one higher and one decrease on either side) will probably be totally up and about to come back involved.
After 2 years it’s tough to evaluate the age of swine by the enamel. Nonetheless, besides within the case of breeding and exhibition animals, it isn’t typically necessary to know the precise age of mature hogs. It’s doable, nonetheless, to affiliate progressive put on of the enamel with the advance in age. Aged swine present appreciable put on of the enamel, particularly of the molars (fig. 31).

[ad_2]
Source link






















