[ad_1]
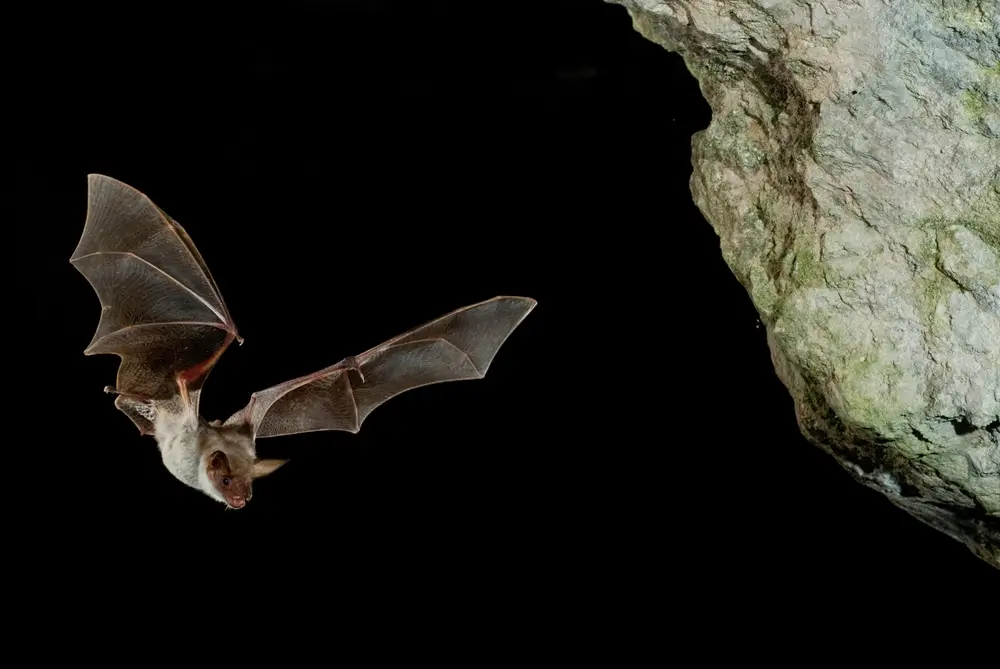
Bats are a fascinating bunch, flying a whole lot of miles, pinpointing prey with sonar and main advanced social lives. They’re additionally voracious predators of bugs wreaking havoc on crops corresponding to cotton, cocoa and rice.
By actually wiping out tons of pests each evening, bats save US farmers an estimated $3.7 billion yearly. Moreover the bug carnage, bats additionally pollinate crops corresponding to coconuts, agave, guava and bananas, disperse seeds and create fertilizer.
Nevertheless, these little mammals are below assault—greater than half of North American bats danger extreme inhabitants declines over the subsequent 15 years. And agriculture, which destroys foraging and roosting habitat, is without doubt one of the best threats to bats.
But farmers might be essential allies for wildlife by utilizing revolutionary practices to preserve bats. In flip, this mammalian air crew protects and pollinates their fields.
Pests and heirloom produce
“I do know lots of people are sort of freaked out by the bats however they’re invaluable in sustainable agriculture—completely invaluable,” says Stephanie Miller, proprietor of Mystic Pine Farm in Virginia, which makes a speciality of natural heirloom crops from the African diaspora.
Her farm is bustling with bat exercise for a number of causes.
“We don’t clearly use any chemical substances as a result of that’s additionally a primary deterrent and that can undoubtedly do away with your bat inhabitants in a short time,” says Miller.
Moreover instantly poisoning bats, pesticides and insect-resistant crops scale back the abundance of their prey.

A wooded space on Mystic Pine Farm in Virginia. (Photograph courtesy of Stephanie Miller)
Miller additionally maintains oaks on her property to offer roosts for the bats and deliberately provides meals for her winged visitors.
“I develop night-blooming vegetation that entice the bats and provides them nectar and feed them,” says Miller. “Additionally, I develop species of native vegetation and what I might think about medicinal herbs that in addition they wish to feed off of or entice the meals that they eat—issues like purple coneflower, yucca and sunflowers.”
Analysis backs these observations up: Lower-intensity practices corresponding to agroforestry and natural farming assist larger bat exercise ranges and variety in comparison with extra intensive agriculture.
Components on the panorama stage additionally come into play.
“It’s best to at all times depart as a lot pure habitat as potential round your farms,” says Merlin Tuttle, a bat researcher and founding father of Merlin Tuttle’s Bat Conservation. “The place pests do the worst injury is the place you may have large monocultures, the place for miles and miles you don’t have anything however corn or soybeans or wheat planted. And in these circumstances, bats and different pure predators can’t survive the low season. After you harvest the corn or the wheat, there’s no pests on the market to eat.”
In flip, Miller advantages from having bats round.
“I’m utilizing nature, together with the bats, to regulate my pest inhabitants,” says Miller. “And bats do loads of work. They really pollinate sure crops. Additionally they eat pests that is likely to be a problem and preserve these populations below management.”
As an example, bats kill corn earworms, a serious pest of popcorn and one among Miller’s primary crops.

“I’m utilizing nature, together with the bats, to regulate my pest inhabitants,” says Virginia farmer Stephanie Miller. (Photograph courtesy of Stephanie Miller)
Pecan safety
Whereas Miller exemplifies a bat-friendly farmer, she’s not alone. By means of Merlin Tuttle’s Bat Conservation and Bat Conservation Worldwide, pecan farmers are studying learn how to lower down on pests by putting in bat homes.
One instance is John Price Byrd, proprietor of a sustainable pecan farm in central Texas.
“We’ve three moth-born pests right here, the walnut caterpillar, the pecan nut casebearer and the hickory shuckworm,” says Byrd. “However the bats, their main meals is moths. So, I believed, nicely that’s nice. Some individuals in Georgia had performed it, put bat homes into their pecan orchards. So, I began placing up bat homes.”
Byrd has 5 species of bats on his property. Some forage in large open areas away from their roosts, whereas others dine regionally within the orchard cover. Whereas all of the bats suppress pecan pests, the locavores kill probably the most.
Byrd makes use of a few methods to assist his bats. Moreover placing up bat bins, he doesn’t spray any pesticides on his property. As well as, if a tree dies in his orchard, he leaves it up.
“Quite a lot of these bats roost in these previous lifeless pecan bushes…” says Byrd.
“The very best bats had been staying in these cavities, not as many numbers just like the [Brazilian] free tails in my homes, however they had been doing so much. They had been native feeders as a substitute of feeding within the ambiance.”
Unsurprisingly, all this pest-munching is efficacious.
“If individuals may truly see what bats are doing, they’d be lined as much as shield them,” says Tuttle. “It’s estimated by our Parks and Wildlife Division right here in Texas that consumption of insect pests is saving Texas farmers roughly $1.4 billion yearly.”
Aiding agaves
One among Mexico’s most iconic merchandise has additionally jumped on the bat conservation bandwagon.
By means of the Tequila Interchange Undertaking, tequila and mezcal producers are rising bat-friendly agaves. These spiky vegetation are usually cloned, however letting a few of them flower has a number of benefits. Evening-blooming flowers present nectar for bats, together with an endangered species, the Mexican long-nosed bat. By feeding on the flowers, bats additionally pollinate them.
Business farming of blue agave, used for tequila, has eroded its genetic range and elevated its susceptibility to illness. As an example, within the Nineties, a mix of micro organism and fungus unfold by agave fields, and practically 25 p.c of the crop was deserted.
This hasn’t gone unnoticed by agave farmers.
“They perceive that one thing is occurring,” says Irene Zapata Moran, a doctoral scholar on the College of Wyoming. “They see that there are extra ailments within the crops. And individuals who have been on this business all their life, they’ve instructed me they bear in mind earlier than that the vegetation was once larger.”

A lesser long-nosed bat feeds on an agave blossom in Arizona. (Photograph: Shutterstock)
Bat pollination is seen as an answer, as a result of versus cloning genetically an identical vegetation, sexual replica brings in new genes. This might additionally enhance the plant’s capacity to adapt to local weather change.
Nevertheless, permitting for pure pollination of agaves entails a direct monetary hit for farmers.
Farmers usually lower the flower stalks on the agave to permit the sugar to be concentrated within the core. After harvesting, they use this core for tequila manufacturing.
“They’re utterly rivals—you can’t have agaves in bloom and tequila from the identical plot,” says Zapata Moran.
One resolution may very well be for tequila producers to cost a premium value for bat-friendly merchandise. Offsetting only a portion of their sunken prices may very well be an efficient option to incentivize farmers who is probably not motivated to surrender a few of their crops within the identify of biodiversity.
The huge swaths of cropland and pasture blanketing the globe current a golden alternative for bat conservation. And, with greater than 18 p.c of species listed as threatened globally, bats want all the assistance they will get. Whereas sustainable practices require funding, cost-sharing packages, corresponding to these from the USDA Pure Sources Conservation Service, may also help farmers. Plus, the payoff is price it—bats are an eco-friendly resolution for a lot of agricultural woes.
[ad_2]
Source link